Two types of contact will result in a person receiving an electric shock. Direct contact with live parts involves touching a terminal or line conductor that is actually live. The regulations call this basic protection.
Indirect contact results from contact with an exposed conductive part such as the metal structure of a piece of equipment that has become live as a result of a fault. The regulations call this fault protection.
Basic protection is protection against electric shock under normal conditions.
IEC 60050-195-2021
Basic protection shall consist of one or more provisions that, under normal conditions, prevent contact with hazardous-live-parts.
NOTE. Paints, varnishes, lacquers and similar products alone are generally not considered to provide adequate insulation for protection against electric shock in normal service.
Below are some individual provisions for basic protection:
- Basic insulation;
- Protective barriers or enclosures;
- Obstacles;
- Placing out of arm’s reach;
- Limitation of voltage;
- Limitation of steady-state touch current and energy;
- Potential grading;
- Other provisions for basic protection.
NOTE. In Portugal for low-voltage installations, systems and equipment, basic protection generally corresponds to protection against direct contact.
Fault protection is protection against electric shock under single fault conditions.
EC 60050-195-2021
Fault protection shall consist of one or more provision(s) independent of and additional to those for basic protection.
Below are some individual provisions for fault protection:
NOTE. In Portugal for low-voltage installations, systems and equipment fault protection generally corresponds to protection against indirect contact.
NOTE. Not all of the protective provisions are applicable to both low-voltage and high-voltage.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between protective measures and their respective provisions for basic protection and fault protection.
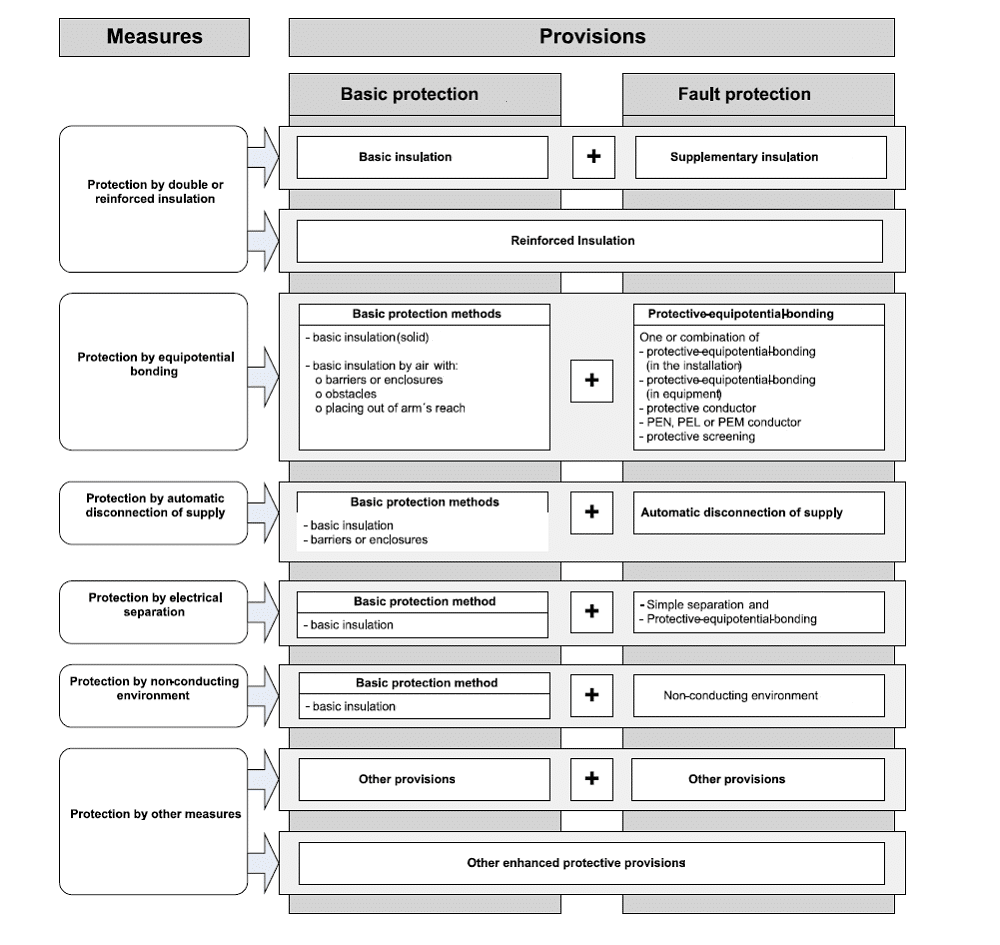 Figure 1 – Protective measures with basic and fault protection
Figure 1 – Protective measures with basic and fault protection
