This surge protective device (SPD) calculator can be used to determine if protection against transient overvoltage from atmospheric origin is required, or not.
1. Select either “RURAL & SUB” (Rural and suburban environment) or “URBAN” (Urban environment).
fenv is an environmental factor and the value of fenv shall be calculated according to Table 443.1 of IEC 60364-4-44-2018.
| Environment | fenv |
| Rural and suburban environment | 85 × F |
| Urban environment | 850 × F |
Table 443.1 [IEC 60364-4-44-2018] – Calculation of fenv
2. The value of coefficient F shall be taken equal to 1 for all installations (by default in the calculator). In the UK and in the Spain, the value of coefficient F shall be taken equal to 1 for all installations. However, National Committees may adjust the value of coefficient F from 1 to 3 for dwellings.
3. Enter a value in “Ng” (In the UK, the lightning ground flash density according to figure 44.2 of BS 7671). This must be greater than 0 but less than 2. Ng is the lightning ground flash density (flash per km2 per year) relevant to the location of the power line and connected structure.
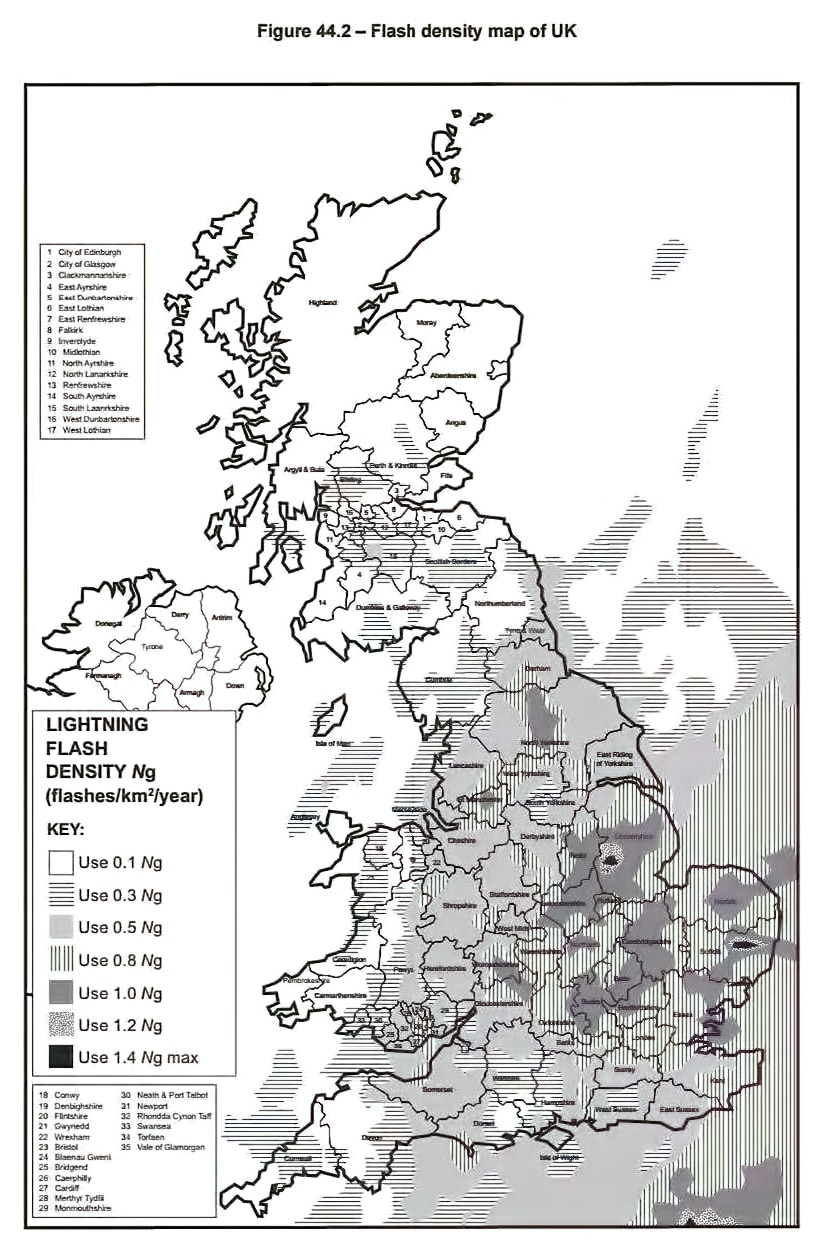 Figure 44.2 of BS 7671 18th Edition
Figure 44.2 of BS 7671 18th Edition
NOTE: According to IEC 62305-2:2010, Clause A.1, 25 thunderstorm days per year are equivalent to a value of 2,5 flashes per km2 per year. This is derived from the formula Ng = 0,1 × Td, where Td is the number of thunderstorm days per year (keraunic level).
4. Enter a value in at least one of the four fields ‘Lpal‘, ‘Lpcl’, ‘Lpah‘ or ‘Lpch‘. Value(s) must be greater than zero and no more than 1.
- LPAL is the length (km) of low-voltage overhead line;
- LPCL is the length (km)of low-voltage underground cable;
- LPAH is the length (km)of high-voltage overhead line;
- LPCH is the length (km)of high-voltage underground cable.
5. Click the “Calculate” button at the bottom left to do the calculation.
6. If you would like to do another calculation, click the “Reset” button to clear all the current data
Calculated risk level (CRL) is used to determine if protection against transient overvoltages of atmospheric origin is required. The CRL is found by the following formula:
CRL = fenv / (LP × Ng)
The risk assessment length LP is calculated as below:
LP = 2 LPAL + LPCL + 0,4 LPAH + 0,2 LPCH
The total length (LPAL + LPCL + LPAH + LPCH) is limited to 1 km or by the distance from the first overvoltage protective device installed in the power network to the entrance of the installation whichever is the smaller.
If the distribution networks lengths are totally or partially unknown then LPAL shall be taken equal to the remaining distance to reach a total length of 1 km.
For example, if only the distance of underground cable is known (e.g. 100 m), then the LPAL shall be taken equal to 90 m. An illustration of an installation showing the lengths to consider is given in Figure 443.1 of IEC 60364-4-44-2018.
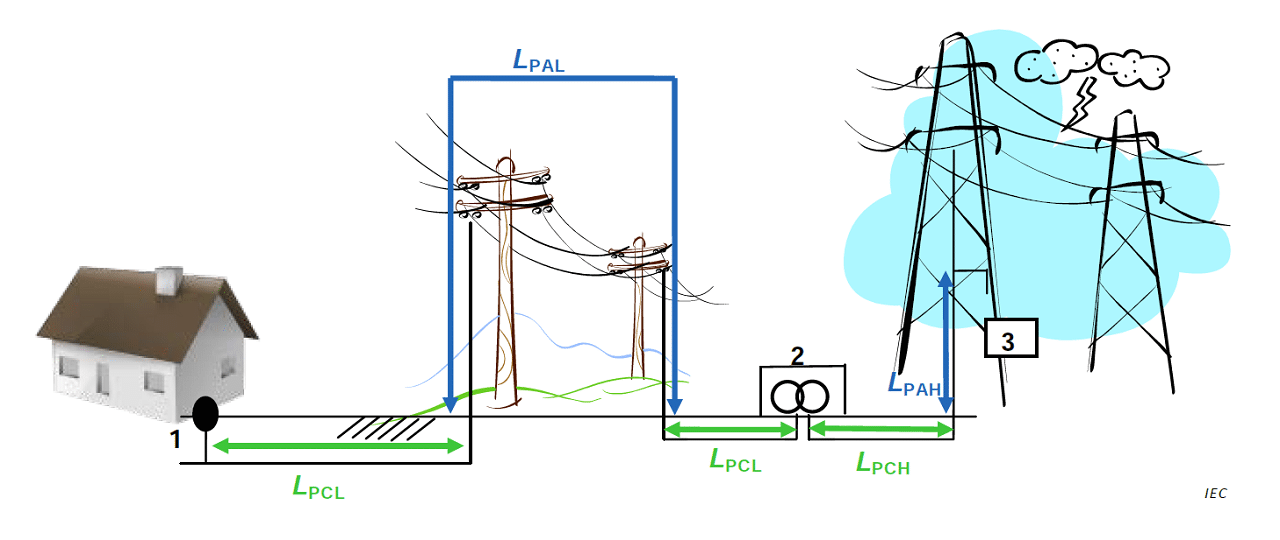 Figure 443.1 – Illustration of an installation showing the lengths to consider [IEC 60364-4-44-2018]
Figure 443.1 – Illustration of an installation showing the lengths to consider [IEC 60364-4-44-2018]
Key:
- 1 origin of the installation
- 2 LV/HV transformer
- 3 surge arrestor (overvoltage protective device)
- If CRL ≥ 1 000, no protection against transient overvoltages of atmospheric origin is needed;
- If CRL < 1 000, protection against transient overvoltages of atmospheric origin is required.
NOTE: In Germany, this CRL calculation and calculator does not apply [according to IEC 60364-4-44-2018].
- Ground flash density Ng = 1
- Environmental factor fenv = 85
Risk assessment length LP = 2 LPAL + LPCL + 0,4 LPAH + 0,2 LPCH = (2 × 0,4) + (0,4 × 0,6) = 1,04
where
- LPAL is the length (km) of low-voltage overhead line= 0,4;
- LPAH is the length (km) of high-voltage overhead line= 0,6;
- LPCL is the length (km) of low-voltage underground cable = 0;
- LPCH is the length (km) of high-voltage underground cable = 0.
CRL = fenv / (LP × Ng) = 85 / (1,04 × 1) = 81,7
In this case, surge protective device (SPD) protection shall be installed as the CRL is less than 1 000.
- Ground flash density Ng = 0,4
- Environmental factor fenv = 85
Risk assessment length LP = 2 LPAL + LPCL + 0,4 LPAH + 0,2 LPCH = 0,2 × 1 = 0,2
where
- LPAL is the length (km) of low-voltage overhead line = 0;
- LPAH is the length (km) of high-voltage overhead line = 0;
- LPCL is the length (km) of low-voltage underground cable = 0;
- LPCH is the length (km) of high-voltage underground cable= 1.
CRL = fenv / (LP × Ng) = 85 / (0,2 × 0,4) = 1 062,5
In this case, SPD protection is not mandatory as the CRL is greater than or equal to 1 000.
- Ground flash density Ng = 1
- Environmental factor fenv = 850
Risk assessment length LP = 2 LPAL + LPCL + 0,4 LPAH + 0,2 LPCH = 2 × 0,4 + 0,4 × 0,6 = 1,04
where
- LPAL is the length (km) of low-voltage overhead line = 0,4;
- LPAH is the length (km) of high-voltage overhead line = 0,6;
- LPCL is the length (km) of low-voltage underground cable = 0;
- LPCH is the length (km) of high-voltage underground cable = 0.
CRL = fenv / (LP × Ng) = 850 / (1 × 1,04) = 817
In this case, SPD protection shall be installed as the CRL is less than 1 000.
- Ground flash density Ng = 0,5
- Environmental factor fenv = 850
Risk assessment length LP = 2 LPAL + LPCL + 0,4 LPAH + 0,2 LPCH = 1
where
- LPAL is the length (km) of low-voltage overhead line = 0;
- LPAH is the length (km) of high-voltage overhead line = 0;
- LPCL is the length (km) of low-voltage underground cable= 1;
- LPCH is the length (km) of high-voltage underground cable = 0.
CRL = fenv / (LP × Ng) = 850 / (1 × 0,5) = 1 700.
In this case, an surge protective device (SPD) is not mandatory as the CRL is greater than or equal to 1 000.
