As an electrical engineer, I often rely on symbols to communicate important information about electrical systems and devices. In thе articlе, wе will еxplore some of thе key physical statе symbols usеd in еlеctrical schеmatics and wiring diagrams. Having a solid understanding of physical state symbols allows engineers to quickly analyze and troubleshoot circuits.
Thе table givе a concisе rеfеrеncе guidе to thе most common physical statе symbols еncountеrеd on thе job.
| Symbol | Description | Application notes |
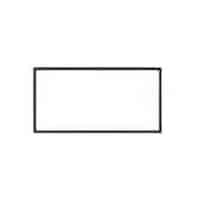 | Name: Material, unspecified Source: IEC 60617-2019 | A1 |
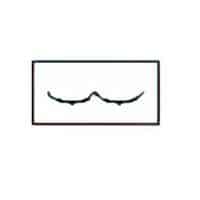
 | Name: Material, gas. Alternative name: Gas (air); pneumatic Source: IEC 60617-2019 or IEEE Std 315-1993 | A1 |
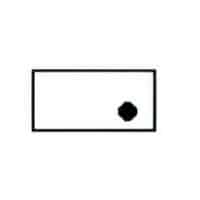
 | Name: Material, liquid Source: IEC 60617-2019 or IEEE Std 315-1993 | A1 |
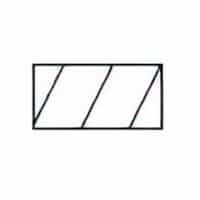 | Name: Material, solid Source: IEC 60617-2019 or IEEE Std 315-1993 | A1 |
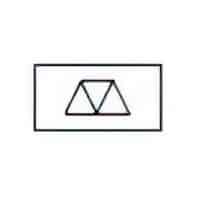 | Name: Material, electret Source: IEC 60617-2019 or IEEE Std 315-1993 | A1 |
| Name: Material, semiconducting Source: IEC 60617-2019 | A1 | |
 | Name: Material, insulating Source: IEC 60617-2019 | A1 |
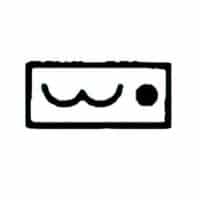 | Name: Gaseous liquid Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 | – |
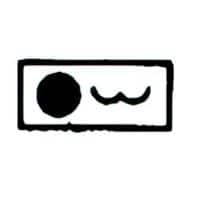 | Name: Steam (or moist gas) Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 | – |
Showing Two or More States
Use only if essential to indicate special condition.
NOTES (for symbols  and
and  ):
):
- A combination of physical state recognition symbols indicates a material in more than one state. The relative sizes and locations of the recognition symbols indicate the normal or predominant state of the device.
- Do not rotate or show in mirror-image form.
Application Notes
A1:
The type of material may be indicated either by using its chemical symbol,or by one of the qualifying symbols given below.
These symbols have been drawn in rectangles, but the rectangle may be omitted when they are used in conjunction with another symbol.
If necessary, use may be made of the symbols for materials given in ISO 128.
