A general diode is a two terminal device which allows an electrical current to pass in one direction and to block it in the other direction.
The diode symbol table below represents the result of my research into regulatory documentation in the area of electrical and electronic symbols.
See also: capacitor symbols ►
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| Name: Semiconductor diode, general symbol Alternative names: semiconductor rectifier diode; metallic rectifie Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 | |
| Name: Semiconductor diode (IEEE style) Alternative names: semiconductor rectifier diode; metallic rectifie Source: IEEE Std 315-1993, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 | |
| Name: Diode, general Source: IPC 2612-2010 | |
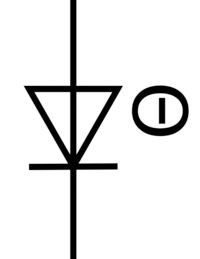 | Name: Temperature sensing diode Alternative name: Temperature-dependent diode Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
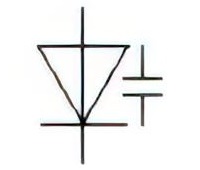 | Name: Variable capacitance diode Alternative name: Varactor Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
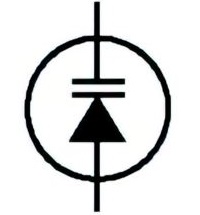 | Name: Capacitive diode (varactor) Source: IEEE Std 315-1993, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
 | Name: Diode, varactor Source: IPC 2612-2010 |
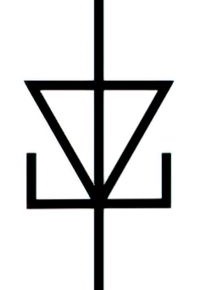 | Name: Tunnel diode Alternative name: Esaki diode Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
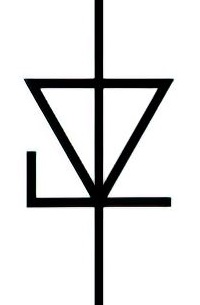 | Name: Breakdown diode, unidirectional Alternative name: Zener diode; Voltage regulator diode Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
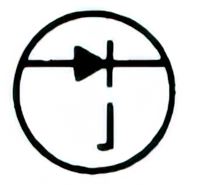 | Name: Unidirectional diode; voltage regulator Source: IEEE Std 315-1993, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
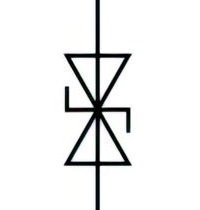 | Name: Breakdown diode, bidirectional Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
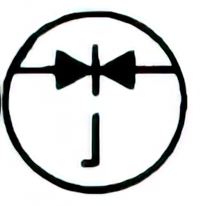 | Name: Bidirectional diode Source: IEEE Std 315-1993, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
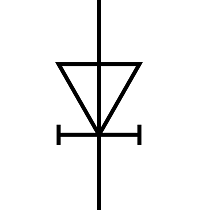 | Name: Backward diode (unitunnel diode) Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
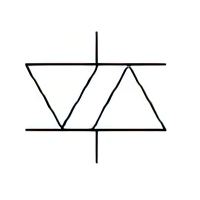 | Name: Bidirectional diode Source: IEC 60617-2019 |
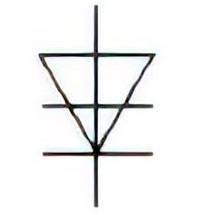 | Name: Reverse blocking diode thyristor Alternative name: Thyristor, reverse-blocking diode-type Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
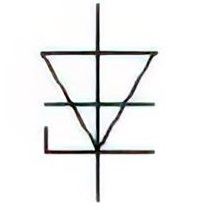 | Name: Reverse conducting diode thyristor Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
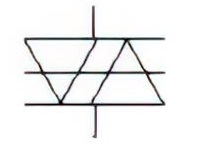 | Name: Bidirectional diode thyristor; Diac Alternative names: Thyristor, bidirectional diode type; bi-switch Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
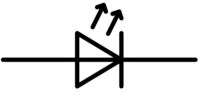 | Name: Light emitting diode (LED), general symbol Alternative name: Photoemissive type diode Remark: See A1 Note Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
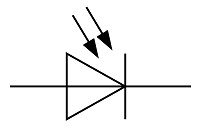 | Name: Photodiode Alternative name: Photosensitive type diode Remark: See A1 Note Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
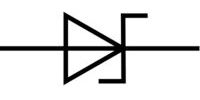 | Name: Schottky diode Source: IEC 60617-2019, ANSI/IEEE Std 315A-1986 |
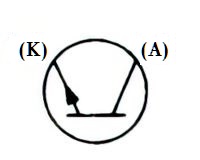 | Name: Unidirectional negative resistance breakdown diode; NPN-type Alternative names: NPN breakdown diode; trigger diac Remark: K – Cathode; A – Anode Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 |
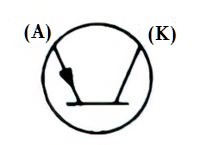 | Name: Unidirectional negative resistance breakdown diode; PNP-type Alternative names: PNP breakdown diode; trigger diac Remark: K – Cathode; A – Anode Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 |
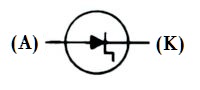 | Name: Step recovery diode Remark: K – Cathode; A – Anode Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 |
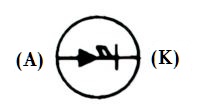 | Name: PIN-type diode Remarks: See A2 Note; K – Cathode; A – Anode Source: IEEE Std 315-1993 |
Application Notes
A1:
If source and target are shown, the arrows shall point from source to target.
If there is a target but no specific source shown, the arrows shall point downwards and to the right.
If there is no specific target shown, the arrows shall point upwards and to the right.
These rules are applied for the original combination of the symbol in the 60617 database which means “Variant A” described in ISO 81714-1. For the other variants, the arrows rotate together with the other elements to keep the position in the whole combination of “Variant A”.
A2:
Use symbol ![]() unless essential to show intrinsic region.
unless essential to show intrinsic region.
